BR Design Principles
This document describes the design principles of Backup & Restore (BR), including its architecture and backup files.
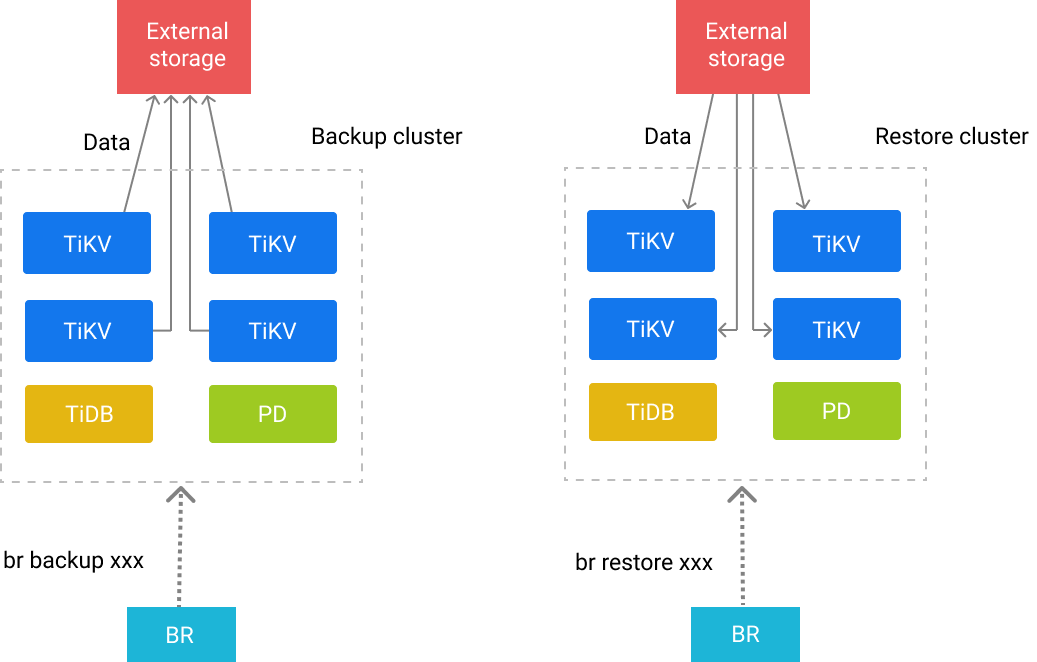
BR architecture
BR sends a backup or restoration command to each TiKV node. After receiving the command, TiKV performs the corresponding backup or restoration operation.
Each TiKV node has a path in which the backup files generated in the backup operation are stored and from which the stored backup files are read during the restoration.
Backup files
This section describes the design of backup files generated by BR.
Types of backup files
BR can generate the following types of backup files:
SSTfile: stores the data that the TiKV node backs up.backupmetafile: stores the metadata of a backup operation, including the number, the key range, the size, and the Hash (sha256) value of the backup files.backup.lockfile: prevents multiple backup operations from storing data to the same directory.
Naming format of SST files
When data is backed up to Google Cloud Storage or Azure Blob Storage, SST files are named in the format of storeID_regionID_regionEpoch_keyHash_timestamp_cf. The fields in the format are explained as follows:
storeIDis the TiKV node ID.regionIDis the Region ID.regionEpochis the version number of a Region.keyHashis the Hash (sha256) value of the startKey of a range, which ensures the uniqueness of a key.timestampis the Unix timestamp of an SST file when it is generated at TiKV.cfindicates the Column Family of RocksDB (defaultorwriteby default).
When data is backed up to Amazon S3 or a network disk, the SST files are named in the format of regionID_regionEpoch_keyHash_timestamp_cf. The fields in the format are explained as follows:
regionIDis the Region ID.regionEpochis the version number of a Region.keyHashis the Hash (sha256) value of the startKey of a range, which ensures the uniqueness of a key.timestampis the Unix timestamp of an SST file when it is generated at TiKV.cfindicates the Column Family of RocksDB (defaultorwriteby default).
Storage format of SST files
- For details about the storage format of SST files, see Rocksdb BlockBasedTable Format.
- For details about the encoding format of backup data in SST files, see Mapping of table data to Key-Value.
Backup file structure
When you back up data to Google Cloud Storage or Azure Blob Storage, the SST files, backupmeta files, and backup.lock files are stored in the same directory in the following structure:
.
└── 20220621
├── backupmeta
|—— backup.lock
├── {storeID}-{regionID}-{regionEpoch}-{keyHash}-{timestamp}-{cf}.sst
├── {storeID}-{regionID}-{regionEpoch}-{keyHash}-{timestamp}-{cf}.sst
└── {storeID}-{regionID}-{regionEpoch}-{keyHash}-{timestamp}-{cf}.sst
When you back up data to Amazon S3 or a network disk, the SST files are stored in sub-directories based on the storeID. The structure is as follows:
.
└── 20220621
├── backupmeta
|—— backup.lock
├── store1
│ └── {regionID}-{regionEpoch}-{keyHash}-{timestamp}-{cf}.sst
├── store100
│ └── {regionID}-{regionEpoch}-{keyHash}-{timestamp}-{cf}.sst
├── store2
│ └── {regionID}-{regionEpoch}-{keyHash}-{timestamp}-{cf}.sst
├── store3
├── store4
└── store5