SET ROLE
The SET ROLE statement is used to enable roles in the current session. After enabling roles, users can use the privileges of the role(s).
Synopsis
SetRoleStmt:

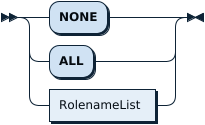
SetRoleOpt:
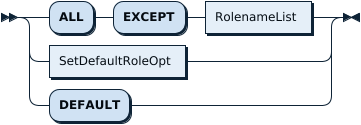
SetDefaultRoleOpt:
Examples
Create a user 'u1'@'%' and three roles: 'r1'@'%', 'r2'@'%' and 'r3'@'%'. Grant these roles to 'u1'@'%' and set 'r1'@'%' as the default role of 'u1'@'%'.
CREATE USER 'u1'@'%';
CREATE ROLE 'r1', 'r2', 'r3';
GRANT 'r1', 'r2', 'r3' TO 'u1'@'%';
SET DEFAULT ROLE 'r1' TO 'u1'@'%';
Log in as 'u1'@'%' and execute the following SET ROLE statement to enable all roles.
SET ROLE ALL;
SELECT CURRENT_ROLE();
+----------------------------+
| CURRENT_ROLE() |
+----------------------------+
| `r1`@`%`,`r2`@`%`,`r3`@`%` |
+----------------------------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
Execute the following SET ROLE statement to enable 'r2' and 'r3'.
SET ROLE 'r2', 'r3';
SELECT CURRENT_ROLE();
+-------------------+
| CURRENT_ROLE() |
+-------------------+
| `r2`@`%`,`r3`@`%` |
+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
Execute the following SET ROLE statement to enable the default role(s).
SET ROLE DEFAULT;
SELECT CURRENT_ROLE();
+----------------+
| CURRENT_ROLE() |
+----------------+
| `r1`@`%` |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
Execute the following SET ROLE statement to cancel all enabled role(s).
SET ROLE NONE;
SELECT CURRENT_ROLE();
+----------------+
| CURRENT_ROLE() |
+----------------+
| |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
MySQL compatibility
This statement is understood to be fully compatible with roles, which are a feature of MySQL 8.0. Any compatibility differences should be reported via an issue on GitHub.